Quantitative Reasoning: A High School Reunion
The questions on this section of the GRE cover the algebra, geometry, and data analysis that is taught in high school. If you were not a math major, you can review those skills by watching our video tutorials and/or working with Brainfuse tutors. If you were a math major, you should still get familiar with the 4 types of questions that you will see on the exam:
A Closer Look at the 4 Types of QR Questions
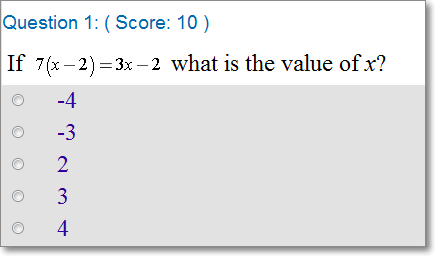
I. Multiple Choice: 1 Answer
These are traditional multiple-choice questions. If you come up with an answer that is not listed, double check the answer choices to see if it is written in a different form—as a fraction instead of a decimal, for example.
Not there? Try the problem again, or use some of the tips below to solve it:

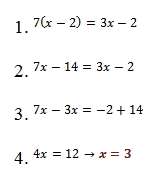
II. Multiple Choice: 1 or More Answers
These problems may have more than one correct answer:Example:


Since the problem said “multiples of either 13 or 15,” we can divide the 2 ostracized[1] choices by 15.

Choices A, B, and E are the answers.
III. Quantitative Comparisons
These are the two questions that you can ask yourself when faced with a quantitative comparison question.
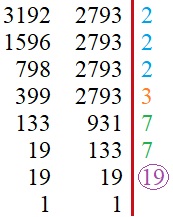
Since 19 is a prime number and is the greatest factor for both numbers, the correct answer is C.
Tips:
IV. Numeric Entries
There are no answer choices for these questions because you’ll type your solution into a box (or 2 boxes if you have a fraction).
Tips:
1. Read the question carefully–what is ETS asking you to find?
2. Plan how to solve the problem.
3. Carry out your plan.
4. Ask yourself if your answer makes sense.

These boxes are a feature on the official GRE exam, but they will not be on the Brainfuse tests. To prepare for these questions, please log on to Live Help and let a Brainfuse tutor know that you would like to work on solving numeric entry questions on the GRE.